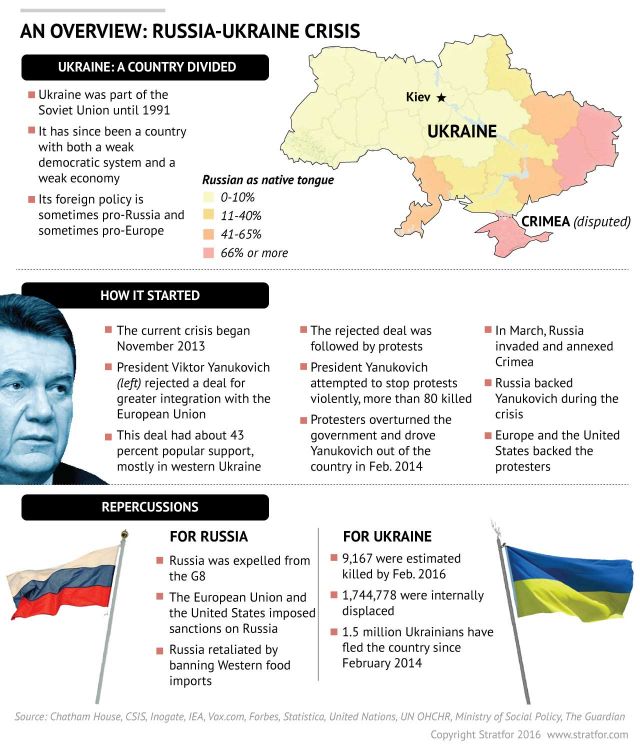
For Ukraine, EU Sanctions on Russia Hang in the Balance, March 21, 2016, Worldview





For Ukraine, EU Sanctions on Russia Hang in the Balance, March 21, 2016, Worldview

Efrem Lukatsky, Russia-Ukraine Tensions,
March 3, 2014, CBS News

Wojtek Radwanski, Ukraine Will Have to Live With Putin's Delusions,
December 2014, Huffpost
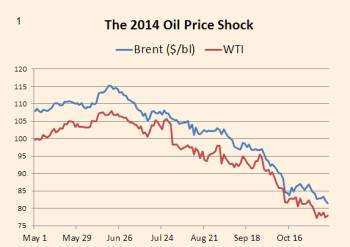
Gavyn Davies, Large Global Benefits from the 2014 Oil Shock, November 12, 2014, Financial Times

David Simonds, Why Russia’s Financial Crises Keep on Coming,
December 21, 2014, the Guardian

Steve Sack, 2014, The Week


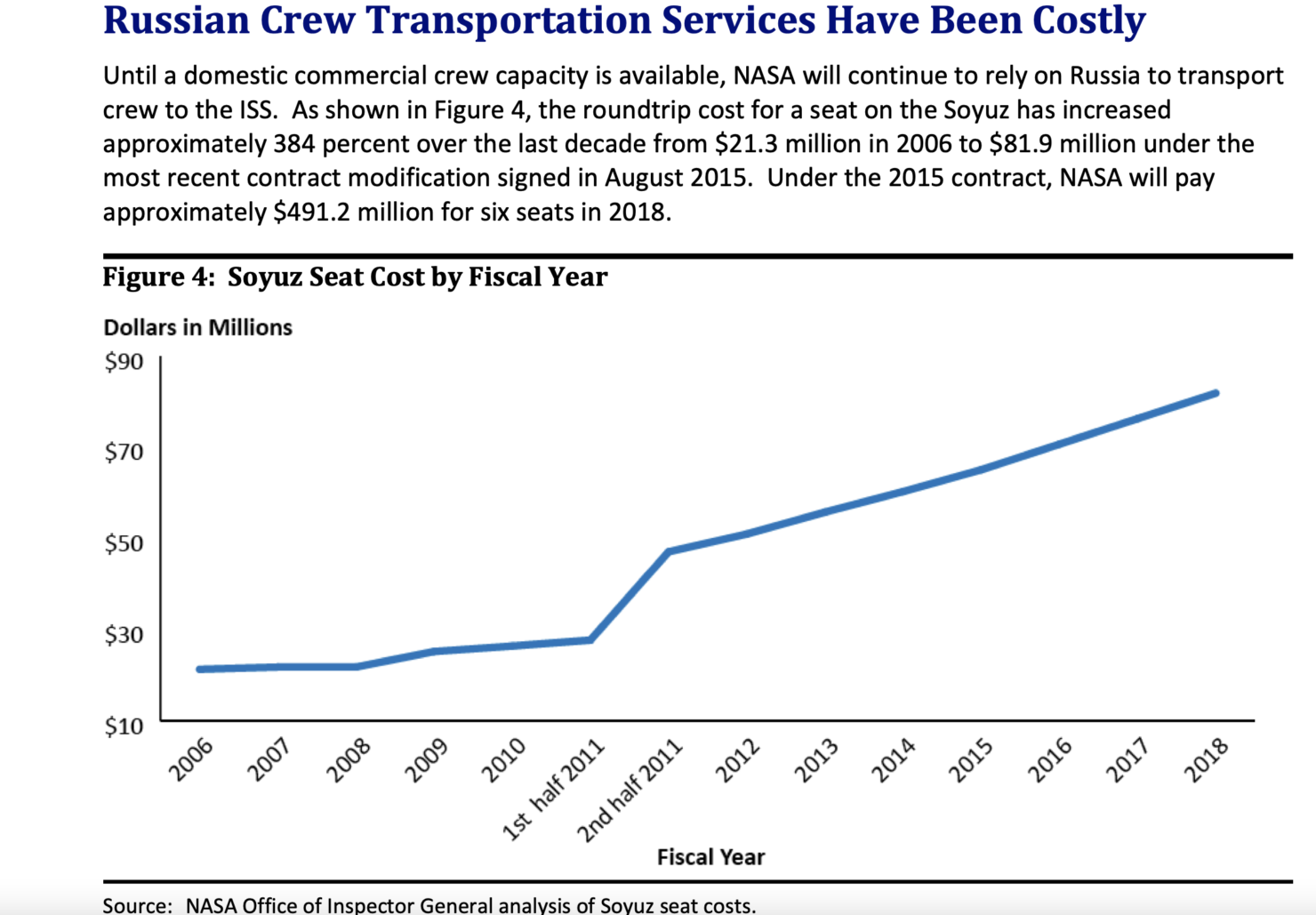
Ramish Zafar, SpaceX Is Qualified To Fly Russian Cosmonauts Says Space Agency Head,
October 25, 2021, NASA
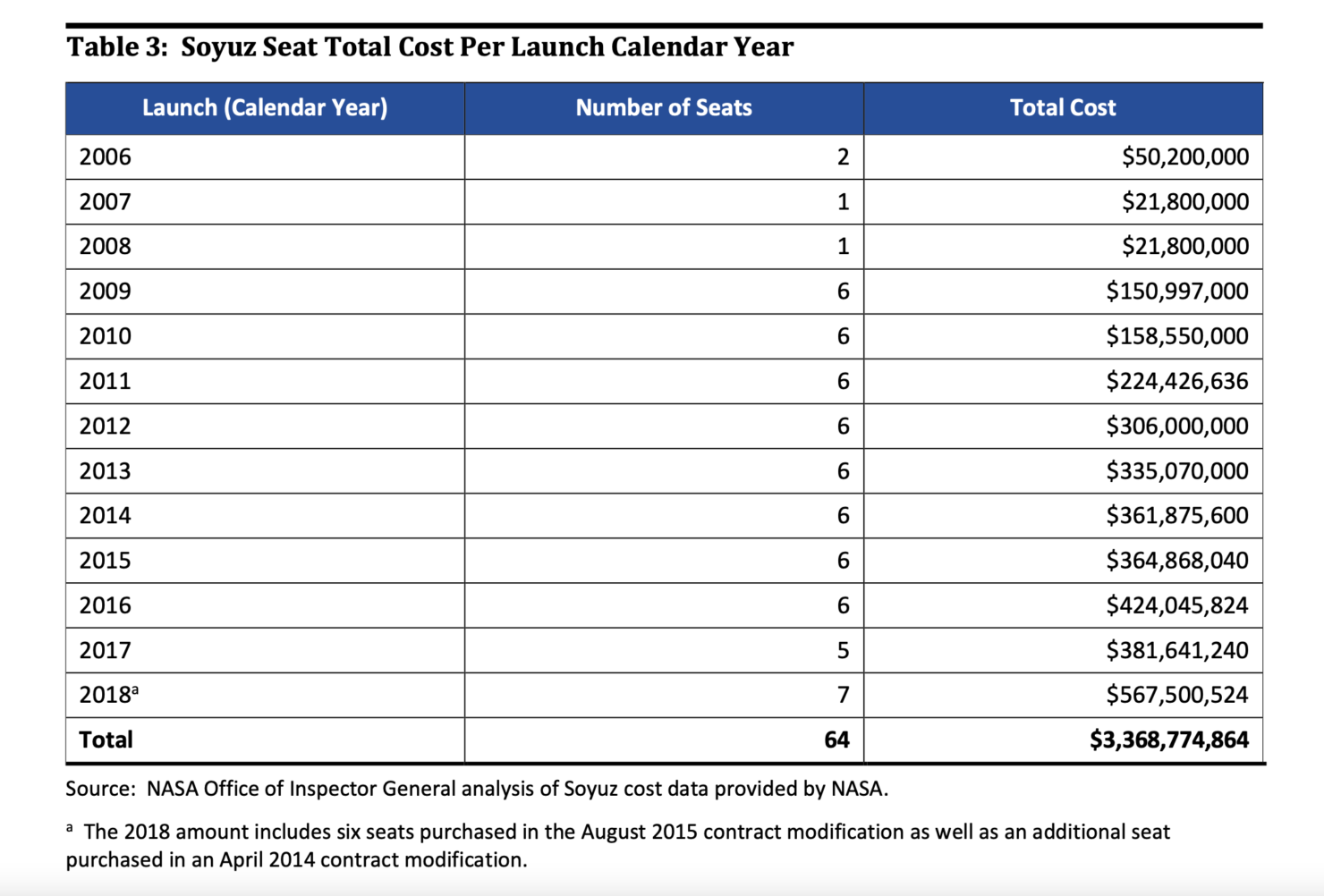
Ramish Zafar, SpaceX Is Qualified To Fly Russian Cosmonauts Says Space Agency Head,
October 25, 2021, NASA

Commercial Crew Program, April 2014, NASA
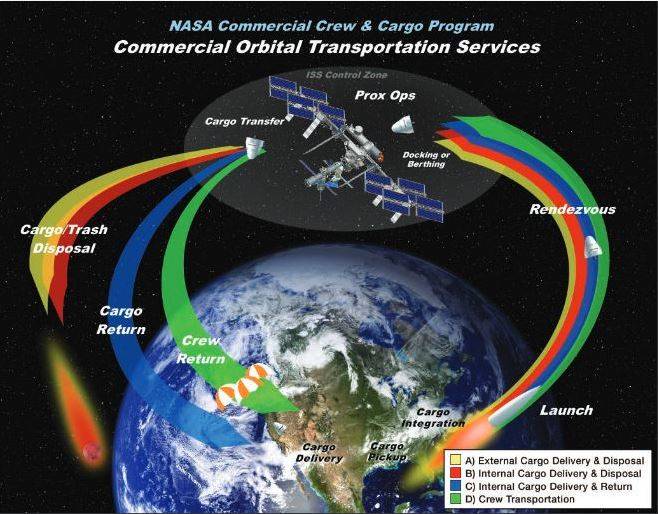
Celebrating the Tenth Anniversary of the COTS Program, August 17, 2016, NASA
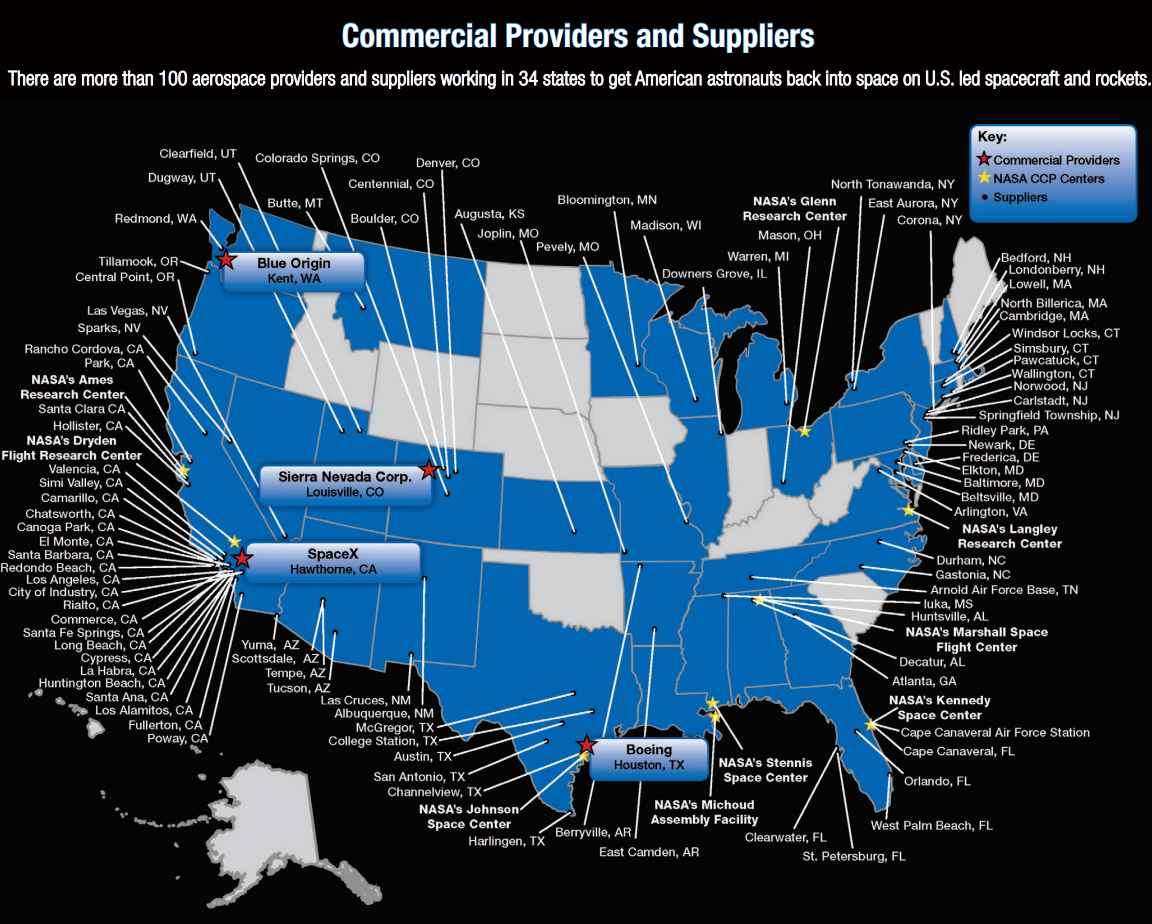
Commercial Crew Program, April 2014, NASA
SpaceX: astronauts arrive at International Space Station on 'recycled' rocket,
April 24, 2021, Guardian News